TL;DR
- Game engines evolved from custom code to universal platforms, revolutionizing development workflows
- Unreal Engine dominates high-end graphics with Lumen, Nanite, and MetaHuman technologies
- Unity excels in accessibility with visual scripting and extensive platform compatibility
- Alternative engines like Godot and O3DE offer free, open-source alternatives with growing communities
- AI integration and cloud-based development represent the next frontier for all major engines
Game engines serve as the comprehensive technical backbone powering every aspect of modern video games, from core physics simulations to advanced visual rendering and audio processing. These sophisticated software frameworks directly determine a game’s technical capabilities, visual fidelity, and overall performance across different hardware configurations.
In the early days of gaming, developers built each title from the ground up, writing custom code for every project. The 1990s witnessed the emergence of the “game engine” concept, primarily driven by the groundbreaking success of Doom and Quake, both developed by id Software utilizing their proprietary id Tech engine. This revolutionary approach enabled other studios to license the core technology while customizing graphics, character designs, and gameplay elements, establishing the foundation for standardized development platforms.
id Software’s contribution continues to resonate throughout the industry, with new iterations of their technology still powering contemporary releases. For instance, DOOM: The Dark Ages, launched in May 2025, was constructed using the eighth generation of this influential engine.
Modern game engines dramatically accelerate development timelines while providing sophisticated tools that streamline complex technical processes. Currently, Unreal Engine and Unity represent the industry’s most widely adopted solutions, each offering distinct advantages for different development scenarios.
Unreal Engine
The Unreal Engine legacy commenced in 1998 when Epic Games debuted their inaugural 3D shooter Unreal, powered by their proprietary UE technology. This foundation spawned numerous legendary titles such as Splinter Cell, Deus Ex, and Lineage II. While graphical excellence has always been UE’s primary focus, continuous evolution has introduced increasingly sophisticated features that enhance both visual quality and development efficiency.
Contemporary Unreal Engine empowers developers to construct projects across virtually every platform imaginable – including PC systems, mobile devices, gaming consoles, VR hardware, and Web3 environments. Simultaneously, Epic has consistently advanced graphical capabilities, enabling unprecedented levels of photorealism through revolutionary technologies including:
- Lumen – facilitates dynamic global illumination with real-time adjustments, enabling realistic light interactions with environmental objects. This innovation significantly streamlines lighting workflow for development teams.
- Nanite – manages virtualized geometry systems, automatically reducing detail complexity at greater distances to optimize performance without compromising visual integrity. The system also enhances loading efficiency and complex scene rendering.
The integrated MetaHuman tool represents another breakthrough, enabling creation of photorealistic 3D characters complete with nuanced facial expressions and natural animations. This technology dramatically simplifies NPC creation pipelines while supporting live facial capture through iPhone integration. MetaHuman Animator combined with Live Link enables developers to animate and voice characters using authentic facial performances.
Unreal Engine facilitates sophisticated NPC behavior systems even for smaller development teams. Developers can construct dynamic worlds where non-player characters make autonomous decisions, respond to player interactions, and react to environmental events. These capabilities are implemented through sophisticated tools including AI Controller, Behavior Trees, Perception System, and EQS (Environment Query System).
As artificial intelligence technology advances, Unreal Engine 5 incorporates increasingly powerful AI-assisted features that accelerate animation production and world building. The engine also supports seamless integration with external AI systems for enhanced content generation.
The integrated Procedural Content Generation (PCG) framework enables automated landscape generation with procedurally placed vegetation, urban environments, ancient ruins, and numerous other elements. AI not only assists in generation processes but also optimizes world structures for enhanced coherence and logical consistency.
Despite its impressive capabilities, Unreal Engine presents certain limitations. The platform demands substantial hardware resources to effectively leverage its extensive feature set. Additionally, projects developed with UE typically exhibit larger file sizes due to high-resolution assets and advanced technological implementations.
Unreal Engine remains freely accessible for all developers. However, once a UE-powered game surpasses $1 million in revenue, developers must pay 5% royalties to Epic Games.
Unreal Engine represents an exceptional development platform that harmonizes creative freedom with technical flexibility. The ongoing integration of AI technologies continues to expand development possibilities while accelerating production timelines. Beyond gaming applications, UE increasingly serves architecture for 3D modeling, film production pipelines, educational simulations, healthcare VR applications, and numerous other industries.
Unity
Unity entered the gaming landscape in 2005 with a mission to democratize game development for creators across all skill levels. The engine supports both 2D and 3D project development across an extensive range of platforms, from traditional computing systems to automotive interfaces.
Unity utilizes C++ and C# as primary programming languages while offering extensive plugin libraries and vibrant community support. These factors established Unity as the premier choice for mobile games development and independent projects. Continuous engine updates, including the sixth version release, have introduced substantial graphical enhancements, AI integration capabilities, and performance optimizations.
Unity’s accessibility stems significantly from its free Unity Personal tier, enabling small developers to realize creative visions without financial barriers. Larger studios typically opt for Unity Pro with additional professional features, while educational usage remains completely free.
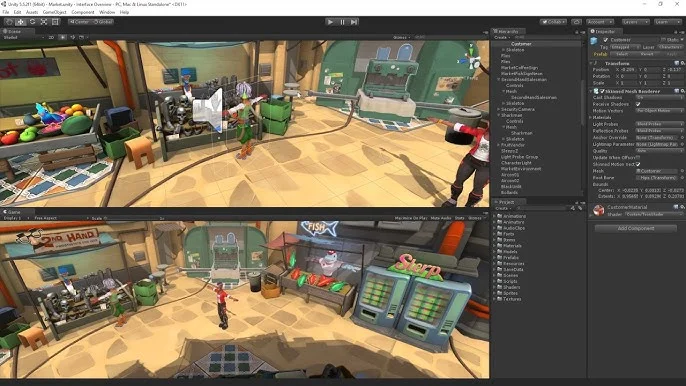
Visual Scripting capabilities further enhance Unity’s appeal for developers with limited programming experience but strong creative ambitions. This node-based visual programming system enables game logic creation without traditional coding, handling animations, character movement, event systems, and numerous other functions. This approach encourages beginners and non-technical enthusiasts to pursue game development using Unity’s accessible framework.
Unity’s future development prioritizes AI technology integration to accelerate project creation. Current initiatives focus on automated code generation, visual content development, and advanced NPC behavior systems.
The recently introduced Unity AI assistant integrates directly into the development environment, capable of writing code snippets, explaining error messages, optimizing existing code, generating scripts from descriptions, and providing contextual suggestions. Through text-based prompts, developers can now generate diverse sound effects, animation sequences, and numerous other assets.
Unity also incorporates Web3 and metaverse integration capabilities. The engine supports Verified SDKs for blockchain implementation while establishing foundations for next-generation metaverse development.
Thus, Unity embodies flexibility, accessibility, and creative realization without demanding extensive programming expertise. The platform includes comprehensive templates enabling developers to create games across genres including indie experiences, runner games, platformers, and roguelike adventures. Despite its already extensive capabilities, Unity’s development team maintains aggressive advancement plans for the engine’s future evolution.
Other Game Engines Worth Watching
Godot
Godot emerged as a relatively recent game engine contender, with its initial version launching in 2014. The platform continues gaining momentum, particularly among independent developers and budget-conscious studios. Godot enables creation of both 2D and 3D games for PC and mobile platforms, with primary advantages including modular architecture and intuitive visual scene editing interfaces.
The engine provides comprehensive feature sets essential for modern game development – including physics simulation, UI development tools, contemporary rendering pipelines, lighting and shadow systems, post-processing effects, and numerous other capabilities. Despite this robust functionality, Godot remains completely free without licensing requirements or royalty obligations.
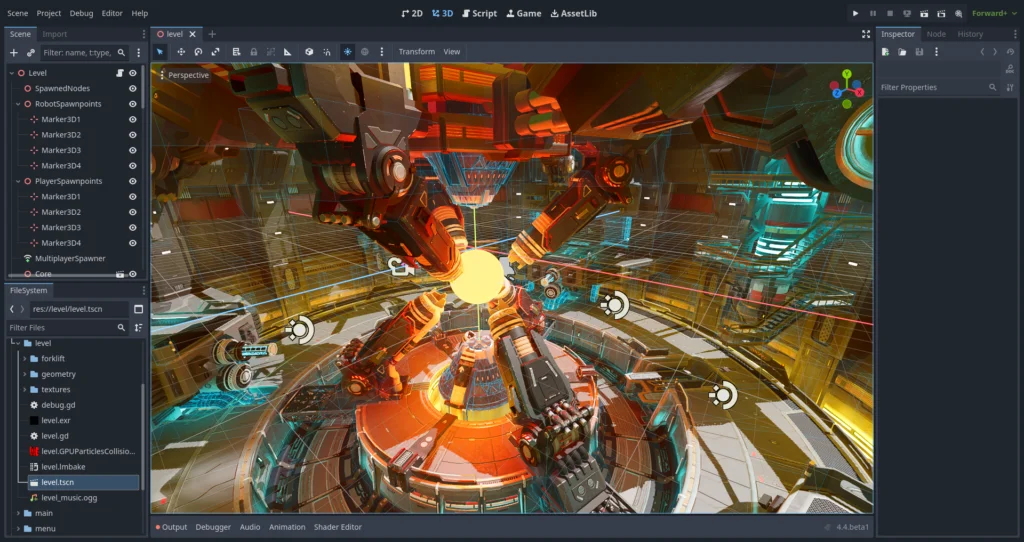
Among notable limitations, Godot currently maintains a smaller developer community compared to established alternatives, with fewer learning resources and documentation available.
CryEngine
CryEngine debuted in 2002 from Crytek, powering the original Far Cry. This engine distinguishes itself through photorealistic graphical capabilities, exceptional lighting systems, sophisticated shading techniques, depth of field effects, and numerous other advanced features.
CryEngine facilitates realistic object interactions within virtual spaces through integrated physics systems. The “Sandbox” editor streamlines game world creation and modification processes.
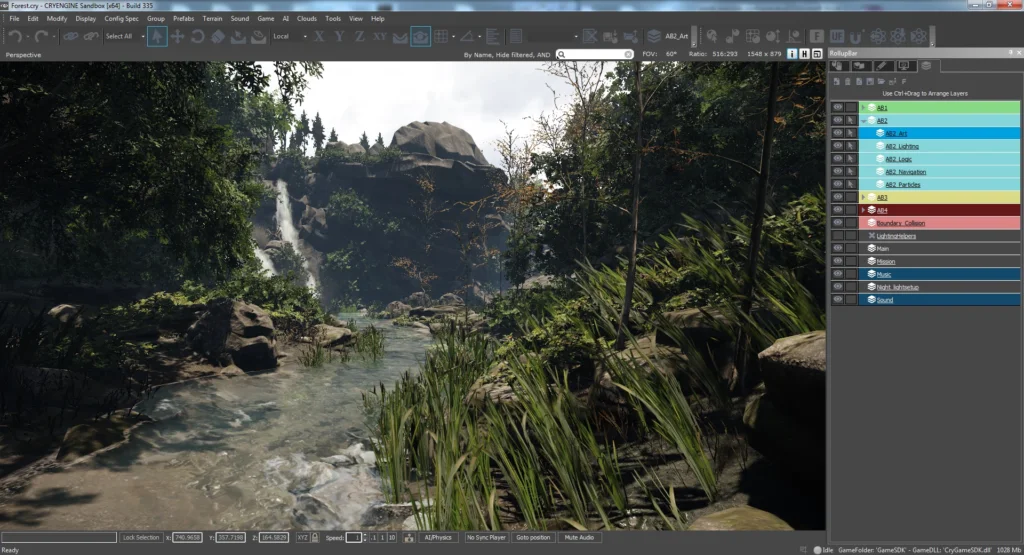
CryEngine primarily excels in first-person shooter development with interactive open-world environments. However, the platform presents significant learning curves, making it more suitable for experienced development teams. The engine also demonstrates limited optimization for mobile project development. These factors contribute to CryEngine’s relatively modest community size.
Amazon Lumberyard / O3DE
The Open 3D Engine (O3DE) represents an intriguing evolution, originally launching as Amazon Lumberyard with CryEngine foundations before transitioning to its current open-source iteration. The engine’s open architecture enables extensive customization to meet specific development requirements, supporting projects of varying complexity across Windows, Linux, Android, iOS, and macOS platforms.
O3DE incorporates powerful visual editing tools, comprehensive scripting systems, advanced physics simulation, and modular structural design. Developers benefit from extensive customization options without licensing costs, while supporting cloud service integration and VR/AR platform compatibility with high-quality rendering and cinematic toolkits.
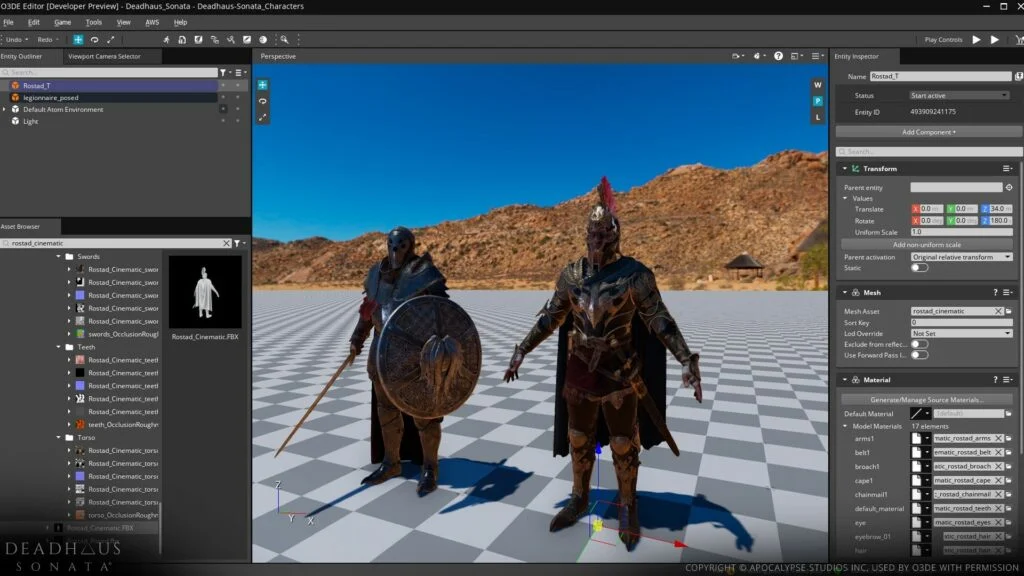
O3DE includes native Amazon Web Services (AWS) support, enabling cloud service integration without complex backend development. The platform also features integrated Twitch functionality for creating interactive broadcast experiences.
The development community recognizes substantial potential in O3DE, noting continuous updates and expanding functionality from its development team. The dedicated advancement of Open 3D Engine positions it as a potential competitor to established platforms like Unity and Unreal Engine within the gaming industry landscape.
Summary
The future trajectory of game engines clearly indicates continued aggressive development across multiple technological frontiers. Artificial intelligence implementation represents a primary direction, focusing on code assistance, level generation, dialogue systems, and numerous other applications. These advancements will accelerate development cycles while creating new opportunities for smaller development studios.
Cloud-based development tools including Unity Cloud and Unreal’s Pixel Streaming will experience significant expansion. These technologies enable project development, testing, and deployment without requiring local hardware infrastructure.
Consequently, modern game engines are evolving beyond gaming applications to become comprehensive platforms for interactive content creation, advanced visualizations, and architectural rendering applications across diverse industries.
Game engines form the technological backbone of modern interactive entertainment, handling everything from physics simulations and audio processing to advanced visual rendering. The choice of engine directly impacts a game’s technical capabilities, visual fidelity, and development timeline, making engine selection one of the most critical decisions for development teams.
During the early days of video game development, studios built each title from the ground up, creating custom codebases for every project. The 1990s witnessed the emergence of the “game engine” concept, primarily within the first-person shooter genre. This shift was largely driven by the massive success of Doom and Quake, both developed by id Software using their proprietary id Tech engine. This led to other developers licensing the core technology and customizing graphics, characters, and gameplay elements, establishing the foundation for universal development platforms that streamlined game creation.
Notably, id Software’s contributions continue to influence the industry today. Their pioneering engine technology remains relevant, with new iterations of gaming engines based on id Tech continuing to emerge. For instance, DOOM: The Dark Ages, released in May 2025, utilized the eighth generation of this foundational engine.
Today’s game engines serve as comprehensive development ecosystems that accelerate and often simplify the creation process. Unreal Engine and Unity currently dominate the market, but several emerging platforms are gaining traction among specific developer communities.
Unreal Engine
The Unreal Engine legacy commenced in 1998 when Epic Games launched the inaugural 3D shooter Unreal, constructed using their proprietary UE technology. It established the groundwork for numerous legendary titles, including Splinter Cell, Deus Ex, and Lineage II. From its inception, UE prioritized graphical innovation, but subsequent evolution introduced comprehensive features that significantly enhanced its capabilities.
Contemporary Unreal Engine empowers developers to construct projects for virtually any platform (PC, mobile devices, consoles, VR, Web3). Simultaneously, its creators have consistently advanced graphical capabilities, delivering unprecedented levels of photorealism through revolutionary technologies including:
- Lumen – facilitates dynamic lighting with real-time adjustments and enables realistic light interaction with environmental objects. This innovation dramatically streamlined developer workflows for in-game lighting systems.
- Nanite – manages visual geometry complexity. It intelligently reduces detail at greater distances, enhancing performance while preserving visual quality. The system also optimizes loading and rendering processes for intricate scenes.
The integrated MetaHuman tool represents another significant advancement within Unreal Engine. This technology streamlines the creation of highly realistic 3D characters complete with nuanced facial expressions and natural animations, significantly simplifying NPC development. MetaHuman additionally supports live facial animation capture, achievable even through iPhone integration. Utilizing MetaHuman Animator + Live Link, developers can animate and voice diverse characters while incorporating genuine facial expressions and movements.
Unreal Engine enables sophisticated NPC behavior creation even for smaller development teams. Developers can construct worlds where non-player characters make autonomous decisions, respond dynamically to player actions, and react to events within the game environment. These capabilities are implemented through specialized tools including AI Controller, Behavior Trees, Perception System, and EQS (Environment Query System).
As artificial intelligence technology progresses, Unreal Engine 5 continues integrating increasingly advanced features that leverage AI to accelerate animation production and world design. The platform also supports integration with external AI systems that assist in generating diverse content types.
The engine incorporates a comprehensive Procedural Content Generation (PCG) framework. This enables developers to generate expansive landscapes with automatically distributed vegetation, urban environments, ancient ruins, and numerous other environmental elements. AI not only facilitates the generation process but also optimizes world structures to ensure visual coherence and logical consistency.
Naturally, Unreal Engine presents certain limitations. For example, the engine demands relatively powerful hardware to efficiently utilize its extensive feature set. Additionally, projects developed with UE tend to have substantial file sizes due to high-quality assets and advanced technological implementations.
Unreal Engine itself remains freely accessible to all developers. However, once revenue generated from a UE-created game surpasses $1 million, developers must remit a 5% royalty fee to Epic Games.
In conclusion, Unreal Engine stands as an exceptional development platform that merges artistic freedom with technical flexibility. Developers are actively incorporating AI technologies that enable continuous evolution and provide new opportunities for accelerated game development. Beyond gaming, Unreal Engine finds increasing application in architectural visualization for 3D model creation, film production pipelines, educational simulations, healthcare VR applications, and numerous other professional domains.
Unity
The development timeline for another prominent game engine – Unity – originated in 2005. This platform was designed with the objective of democratizing game development for broader creative audiences. It supports both 2D and 3D game creation across extensive platform ranges, spanning from personal computers to automotive infotainment systems.
The engine primarily utilizes C++ and C# programming languages. Unity also provides an extensive plugin ecosystem and vibrant community, factors that contributed to its establishment as the preferred solution for mobile game development and independent projects.
As we progress through 2025, Unity maintains its position as the leading platform for developing mobile games. This leadership position is reinforced by continuous engine updates – with the launch of version six, significant enhancements arrived in graphical technologies, AI integration capabilities, and overall performance optimization.
A primary factor driving Unity’s popularity among smaller development teams is the availability of the free Unity Personal edition. Naturally, larger studios may select Unity Pro, which offers expanded functionality, but even the basic version enables developers to realize their creative visions. Furthermore, educational usage of the engine remains completely free of charge.

Visual Scripting support significantly enhances Unity’s appeal for developers possessing minimal programming experience but abundant creative ambition. This system enables game logic construction without traditional coding, utilizing node-based interfaces that manage animations, character movement, event systems, and numerous other functions. This approach empowers beginners and non-technical enthusiasts to develop games using Unity’s intuitive workflow.
Unity’s future development trajectory centers on aggressive advancement of AI technologies designed to accelerate project development cycles. Current emphasis areas include automated code generation, visual content development pipelines, and sophisticated NPC behavior systems.
Recently, Unity introduced Unity AI – an integrated artificial intelligence assistant within the engine environment. This tool can generate code, explain error messages, assist with code optimization, create scripts from descriptive prompts, and provide valuable development suggestions. Through textual input commands, developers can now generate diverse sound effects, animation sequences, and numerous other creative assets.
Unity additionally incorporates Web3 and metaverse integration capabilities. The engine supports Verified SDKs for blockchain technology integration and is establishing foundational infrastructure for next-generation metaverse development.
Thus, Unity embodies flexibility, accessibility, and the capacity to transform creative concepts into playable experiences without requiring extensive programming expertise. The platform already includes comprehensive templates that enable developers to construct their own games across genres including indie, runner, platformer, and roguelike. Despite its already comprehensive capabilities, the development team maintains aggressive advancement plans and continues driving Unity’s technological evolution forward.
Other Game Engines Worth Watching
Godot
Godot represents a comparatively recent addition to the game engine landscape, with its initial version launching in 2014. It is presently experiencing growing adoption, particularly among independent developers and studios operating with constrained budgets. This platform facilitates creation of both 2D and 3D games targeting PC and mobile platforms. For many developers, Godot’s principal advantages reside in its modular architectural design and exceptionally intuitive, user-friendly visual scene editor.
The engine delivers all fundamental features necessary for contemporary game development – including physics simulation support, user interface development tools, modern rendering pipelines, lighting and shadow systems, post-processing effects, and numerous additional capabilities. Despite this comprehensive functionality, Godot remains completely free for commercial usage, requiring neither licensing fees nor revenue-sharing royalties.
Godot’s development team maintains continuous engine improvement efforts. With each successive version release, performance metrics advance, and additional tools integrate – attracting progressively greater interest from independent development communities.

Among the platform’s limitations, developers should note that Godot currently lacks extensive developer community support and provides fewer learning resources and documentation compared to established engines like Unity or Unreal.
CryEngine
The CryEngine platform debuted through Crytek in 2002, serving as the foundation for the original installment of Far Cry. This engine captures attention through its photorealistic graphical capabilities, while also delivering exceptional lighting systems, shading techniques, depth of field effects, and numerous additional visual features.
Additionally, CryEngine enables realistic object interaction within virtual spaces, facilitated by its integrated physics simulation system. The “Sandbox” editing environment streamlines game world creation and modification processes.

CryEngine primarily excels for developing first-person shooters featuring interactive and expansive game worlds. However, it presents the challenge of significant learning complexity, making it more approachable for experienced development professionals. The platform also demonstrates limited adaptation suitability for mobile gaming projects. These factors collectively contribute to CryEngine’s relatively small community ecosystem.
Amazon Lumberyard / O3DE
Next we examine the Open 3D Engine platform. Interestingly, this engine originated as Amazon Lumberyard and was constructed based on CryEngine technology; subsequently, it evolved into O3DE. A significant advantage of this platform is its open architectural design, enabling adaptation to specific developer requirements and supporting game development of any complexity level. It accommodates projects targeting Windows, Linux, Android, iOS, and macOS operating systems.
O3DE incorporates a powerful visual editing environment, comprehensive scripting system, advanced physics simulation, and modular structural design. Developers also benefit from extensive customization possibilities, and the platform imposes no licensing costs. The engine additionally supports integration with cloud service platforms and VR/AR systems, features high-quality rendering capabilities, and cinematic production tools.

The platform includes native support for Amazon Web Services (AWS), enabling cloud service integration without requiring complex backend service development. The system also incorporates integrated Twitch platform support, facilitating creation of interactive gaming experiences for streaming audiences.
The development community recognizes substantial potential within this engine, observing that its creators maintain consistent update cycles and expand development possibilities. The meticulous development investment in Open 3D Engine will ultimately enable it to compete with Unity and Unreal Engine and emerge as one of the premier platforms within the video game industry.
Summary
When considering the future evolution of game engines, it becomes evident that active development will continue accelerating. One primary direction involves implementing artificial intelligence for code development assistance, level generation, dialogue creation, and numerous additional applications. This acceleration will streamline game development workflows and create new opportunities for smaller development teams.
Cloud-based development tools including Unity Cloud and Unreal’s Pixel Streaming technology will also experience continued advancement. This evolution will enable developers to collaborate on projects, conduct testing, and launch games without dependency on local hardware infrastructure.
Consequently, contemporary game engines may transform into comprehensive platforms supporting not only game development but also interactive content creation, diverse visualization projects, and architectural rendering applications.
Action Checklist
- Evaluate project scope and target platforms before selecting an engine
- Assess team expertise and budget constraints against engine requirements
- Test engine performance with prototype projects before full commitment
- Explore community resources and documentation for your chosen engine
- Implement gradual AI tool integration to enhance development workflows
- Evaluate project requirements against engine capabilities including 2D/3D support, platform targets, and graphical needs
- Test engine performance with your specific hardware configuration before commitment
- Assess community support and learning resources availability for your chosen platform
- Explore visual scripting and AI assistant features to accelerate development workflow
- Review licensing terms and revenue sharing requirements for commercial projects
No reproduction without permission:Tsp Game Club » The future of game engines: trends, predictions and history Unleash next-gen gaming with evolving engines, AI, and cloud-powered development.
